|
determine drug absorption by pKa |
|
|
determine drug absorption by pKa |
|
Example
1) The pH of the stomach is 2.5. The pKa of sodium pentothal is 7.4 and it is acidic. If a patient is given sodium pentothal orally instead of IV, will it put the patient to sleep? See the example below:
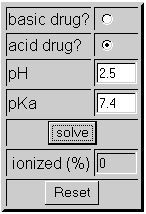
None of the sodium pentothal is ionized in the stomach. Therefore the patient would absorb 100% of this medication and it would put him to sleep.
2) A basic drug with a pKa of 7.8 is a known teratogen. If given IV to a pregnant woman whose blood pH is 7.4, will this drug cross the placenta and effect the baby? See the example below:
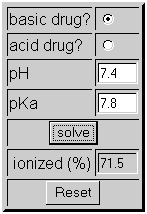
In this example, 72% of the drug is ionized which means 28% of the drug is unionized and will pass through the placenta to effect the baby.
Basics on Ionization
Ionized = water soluble = poor absorption through stomach, BBB, and placenta.
Non-ionized = lipid soluble = absorbed well (cell membranes are composed of lipids)
For example, sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) are both ionized. Cells must provide a channel for these ions to enter an otherwise impenetrable lipid membrane.
Formula
Percent Ionized Formula
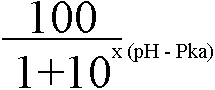
where x = -1 if acid drug or 1 if basic drug
Basic Rules
|
pKa is defined as the pH were a drug exists as 50% ionized and 50% unionized |
|
If pKa - pH = 0, then 50% of drug is ionized and 50% is unionized |
|
An acid in an acid solution will not ionize |
|
If pKa - pH = 0.5, then the solution is 75% ionized/
25% unionized or |
|
If pKa - pH > 1 then the solution is 99-100% ionized or 99-100% unionized* Slight discrepancy between this statement and formula used for calculator. Formula used indicates solutions would be 90-100% ionized or unionized. These rules were taken from my Nursing 605 course. My chemistry background is weak and I'm unable to verify the formula used. Other than this, the formula follows the basic rules. |
Formula provided by Mark Earll
|
manuelsweb.com |